How Do Lead-Acid Batteries Work? A Simple Guide for 2025
Published on July 8, 2025 | by EV Battery School
Introduction
Lead-acid batteries have been powering vehicles and backup systems for over a century. While lithium batteries dominate modern EVs, lead-acid batteries are still relevant today—especially for starter batteries, backup power, and solar storage.
In this article, you’ll learn how a lead-acid battery works, what it’s made of, where it’s used, and how to maintain it for maximum performance. If you’ve ever wondered whether a lead-acid battery is still worth considering, this guide is for you.
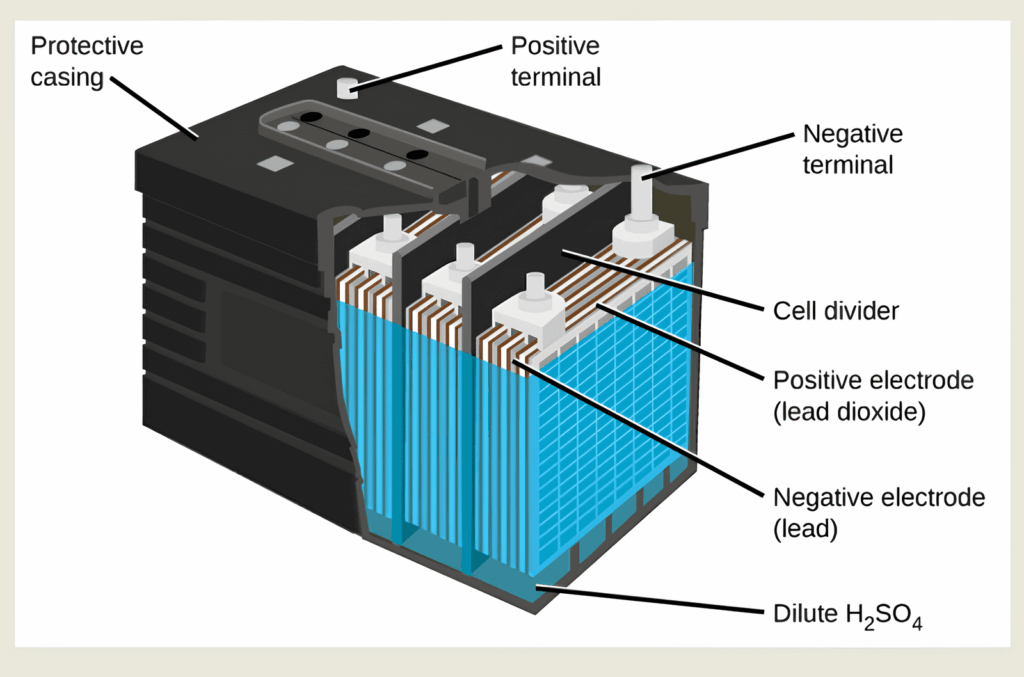
1. Core Components of a Lead-Acid Battery
A typical lead-acid battery contains:
- Positive plates: Lead dioxide (PbO₂)
- Negative plates: Sponge lead (Pb)
- Electrolyte: Diluted sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
These components sit inside each cell and enable a chemical reaction that generates electricity.
2. How Lead-Acid Batteries Generate Power
When discharging, a lead-acid battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy via:
- Positive plate reacts with sulfuric acid to release electrons.
- Electrons flow to the negative plate through your device (starter, UPS, etc.).
- Result: electric current that powers your application.
Charging reverses this process, restoring the battery’s original state.
3. Lead-Acid vs Lithium: Which One is Right for You?
| Feature | Lead-Acid | Lithium |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Life | 300–500 | 2,000+ |
| Cost | Lower upfront | Higher upfront |
| Maintenance | Needs regular check | Low maintenance |
| Energy Density | Lower | Higher |
| Temperature Resistance | Good | Moderate |
If you’re budget-conscious or need a dependable backup solution, lead-acid still makes sense in 2025.

4. How to Extend the Life of a Lead-Acid Battery
To get the most from your battery:
- Recharge promptly after discharge
- Keep terminals clean and corrosion-free
- Avoid deep discharge whenever possible
- Store in cool, dry place during off-seasons
Use our battery cycle life calculator to estimate your usage lifespan.
5. Common Use Cases in 2025
Lead-acid batteries are still found in:
- Gasoline and diesel vehicles
- Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems
- Home solar energy storage setups
- Electric wheelchairs, scooters, and golf carts
FAQ
Q: Are lead-acid batteries still good for EVs?
In small EVs or low-speed vehicles like golf carts, yes. But lithium batteries are preferred for full-sized EVs due to higher energy density.
Q: Can I replace my car battery with lithium?
Yes, but you need a lithium battery with a built-in BMS. Learn more in our Battery Guides.
Conclusion
Lead-acid batteries may not be cutting-edge, but they remain relevant, cost-effective, and dependable. Knowing how they work empowers you to make smarter energy choices—whether you’re powering an old pickup truck or preparing for outages.
Want to go deeper? Explore our Battery Guides and check out our Charging Tips to improve battery health.




