Yes, electric vehicle (EV) batteries are recyclable.
But do you know
How Long It Lasts and How to Extend ev battery life?
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming a common sight on city streets around the world. They are quiet, clean, and efficient, with one major component determining their overall performance — the electric car battery. Whether you drive a compact EV or a larger electric SUV, understanding your battery’s life expectancy, maintenance needs, and replacement cost is essential.
But how long does an electric car battery last? What affects its lifespan? And what can you do to make sure it performs well for years to come? This article answers those questions and gives practical tips to help you get the most out of your EV investment.

1. How Long Does an Electric Car Battery Last?
Most modern lithium-ion batteries used in electric cars last between 8 to 15 years, depending on the vehicle model, climate, and driving habits. In mileage terms, that typically translates to 100,000 to 200,000 miles before noticeable capacity loss.
Unlike lead-acid or nickel-metal hydride batteries, lithium-ion technology offers a high energy density, better efficiency, and slower degradation. That’s why almost all new electric vehicles—from Tesla and BYD to Nissan and Hyundai—use lithium-ion packs.
Manufacturers design these batteries to withstand thousands of charging cycles. A full charging cycle happens when a battery is charged from 0% to 100%. Most drivers don’t fully drain their batteries every day, which extends overall battery life.
| Vehicle Type | Typical Battery Capacity | Estimated Range (per charge) | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact city EV | 30–40 kWh | 150–200 km | 8–10 years |
| Mid-size EV | 50–70 kWh | 250–350 km | 10–12 years |
| Premium EV | 75–100 kWh | 400–500 km | 12–15 years |
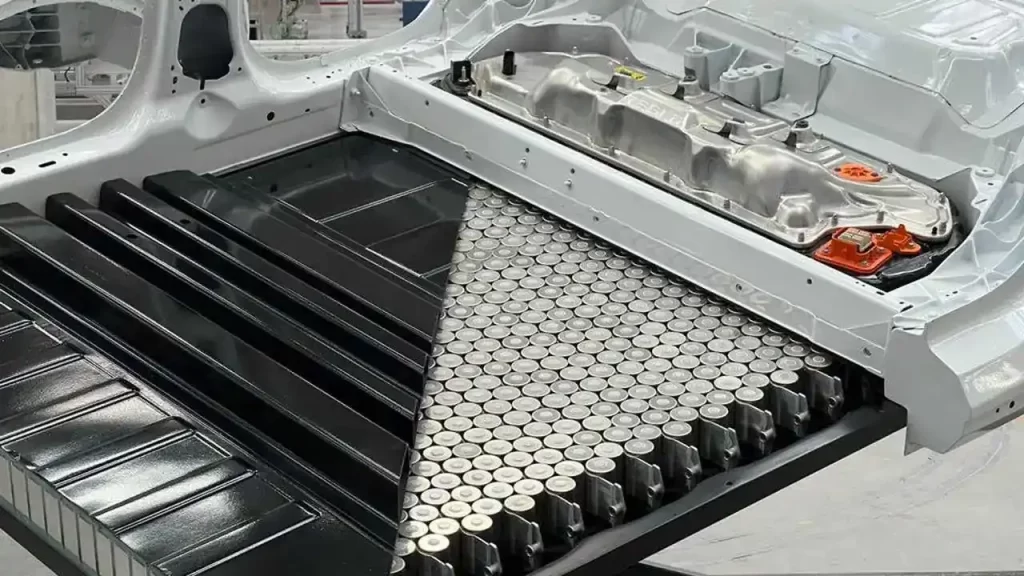

2. How to Estimate Your Electric Car’s Driving Range
Your EV’s battery capacity (measured in kilowatt-hours or kWh) directly determines how far you can travel on a single charge.
A simple formula to estimate your range is:
Range (km) = Battery capacity (kWh) × Efficiency (km per kWh)
For example, if your EV has a 60 kWh battery and consumes 6 km per kWh, the estimated driving range is 60 × 6 = 360 km per full charge.
However, real-world conditions can reduce that number. Factors that affect range include:
Driving speed – High speeds consume more energy.
Weather – Cold temperatures can reduce range by up to 30%.
Air conditioning or heating – HVAC systems use extra power.
Load weight – Carrying passengers or cargo increases energy use.
Terrain – Hills and rough roads consume more electricity.
You can use a battery calculator to estimate how far your electric car can go on a full charge based on driving style and weather conditions.
That’s why electric car battery capacity and battery efficiency are both important when choosing an EV.
3. What Causes Battery Degradation?
Battery degradation is a gradual loss of total capacity over time. A new battery might store 100% of its original energy, but after a few years, it might only hold 90%. This process happens naturally, but certain habits can speed it up.
Common causes include:
Frequent fast charging: High-voltage DC fast chargers heat the battery and accelerate chemical wear.
Extreme temperatures: Prolonged exposure to very hot or cold conditions reduces cell life.
Deep discharging: Regularly draining your battery below 10% shortens its life.
Improper storage: Leaving your EV unused for long periods at full charge or completely empty harms the cells.
If you want to understand how different charge cycles affect capacity, try using a battery cycle life calculator. It helps predict how your battery’s health changes based on usage patterns.
4. How to Extend the Life of Your Electric Car Battery
To maximize battery life and delay the need for replacement, consider the following proven practices:
1. Avoid frequent fast charging
Fast charging is convenient but generates more heat than slow (Level 2) charging. Use it only when necessary, such as during long trips.
2. Keep charge levels between 20% and 80%
Avoid letting the battery drop to 0% or stay at 100% for too long. Many EVs allow you to set a charge limit in the onboard menu.
3. Park in shaded or moderate-temperature areas
Extreme heat can damage cells over time. If possible, use covered parking or garages, especially during summer.
4. Drive smoothly
Rapid acceleration and sudden braking increase power consumption and wear. Gentle driving extends both range and battery health.
5. Use regenerative braking
Regenerative braking captures kinetic energy when slowing down and feeds it back into the battery. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces brake wear.
6. Maintain regular software updates
Manufacturers often release firmware updates that optimize charging and thermal management, which can improve long-term performance.
5. What Happens After an Accident?
After a serious collision, a damaged EV battery may retain residual or stored energy, which poses safety risks. This is known as “stranded energy.” It can cause electric shock or fire if not handled correctly.
Qualified technicians use specialized battery tester tools and high-voltage PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) to safely disconnect or discharge the battery before repair or recycling. Always follow professional guidance — expired PPE should never be used, even if unopened.
6. How Much Does It Cost to Replace an Electric Car Battery?
Battery replacement costs depend on size, chemistry, and brand.
| Type | Capacity | Approx. Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Small city EV | 20–30 kWh | $3,000 – $5,000 |
| Mid-size EV | 40–60 kWh | $6,000 – $9,000 |
| Long-range EV | 75–100 kWh | $10,000 – $16,000 |
While replacement can be expensive, most manufacturers offer 8-year or 100,000-mile warranties, which usually cover significant degradation.
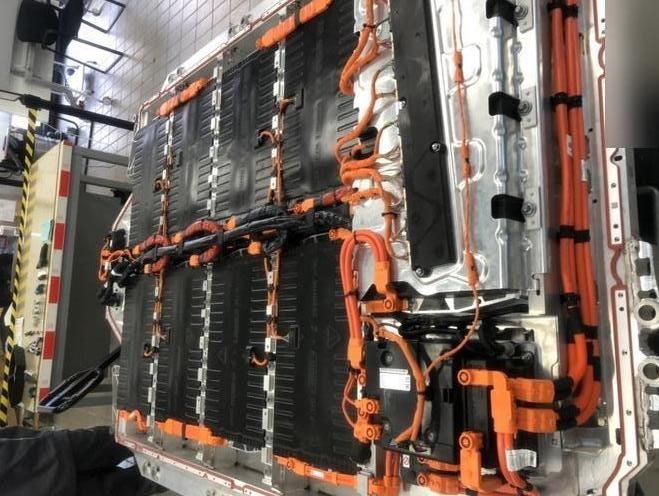

7. The Future of Electric Car Batteries
The industry is rapidly evolving toward solid-state batteries, sodium-ion chemistry, and fast-charging solutions that reduce degradation. These technologies promise higher energy density, safer operation, and longer lifespan.
Companies like Toyota, CATL, and BYD are investing heavily in next-generation batteries that could last up to 20 years with minimal performance loss. As innovation continues, electric vehicles will become more affordable, efficient, and sustainable.
Conclusion
Your electric car battery is the heart of your vehicle — powerful, efficient, and built to last. By understanding its capacity, managing your charging habits, and maintaining it properly, you can extend its lifespan for many years.
EVs represent the future of urban mobility — clean, quiet, and cost-effective. And with smart battery care, you’ll ensure your car keeps running efficiently long after the warranty expires.
References
U.S. Department of Energy – Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy
International Energy Agency – Global EV Outlook
Battery University – Battery Care and Maintenance
Tesla, Nissan, and BYD official documentation
However, A new option for urban commuting: You don’t have to spend tens of thousands of dollars on a large electric vehicle. This enclosed electric four-wheeler, designed for one person, can be yours for just a few thousand dollars, offering a comfortable ride and perfect for everyday commuting. Limited-time offer: Click the link below to purchase now and enjoy special exemptions from purchase tax and VAT!